ELISA Kit DIY Materials for Cross Linked N-Telopeptide Of Type I Collagen (NTXI) 
NTX-I; NTX1
- UOM
- FOB US$ 1,231.00 US$ 2,052.00 US$ 3,694.00 US$ 7,182.00 US$ 12,312.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.KSA639Ra11
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsMain materials for "Do It (ELISA Kit) Yourself".
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayBone metabolism
- Reagent Contents Capture Antibody, Biotin-labeled Competitor, Standard, Streptavidin-HRP, TMB Substrate, 96-well Plate
- Detectable SampleSerum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids.
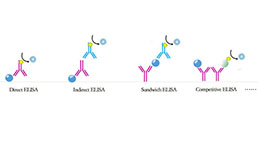
- Applicable PrincipleCompetitive Inhibition ELISA for Antigen Detection
- Detectable Range2.47-200ng/mL
- Applicable Sensitivity0.89ng/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The Abs in the kit have high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Cross Linked N-Telopeptide Of Type I Collagen (NTXI). No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Cross Linked N-Telopeptide Of Type I Collagen (NTXI) and analogues was observed.
Usage
1. Coat the plates with 100μL per well of working solution of Capture Antibody.incubate overnight at 4°C or incubate at 37°C for 2 hours.
2. Aspirate and wash 1 time.
3. Block the plates with 200 μL per well of working solution of Blocking Buffer. Incubate at 37°C for 1.5 hours.
4. Aspirate and wash 1 time. The plates are now ready for sample detection, the protocol is the same as regular ELISA.
Storage
Antibodies, Standard and Streptavidin-HRP should be stored at -20°C. TMB should be stored at 4°C. 96-well Plate could be stored at room temperature. The contents are valid for twelve months. They are stable for one month after opening when stored at 4°C.
Support pack
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Dyslipidemic high-fat diet affects adversely bone metabolism in mice associated with impaired antioxidant capacityScienceDirect: S0899900709004717
- Differential mRNA expression profiles in proximal tibia of aged rats in response to ovariectomy and low-Ca dietScienceDirect: S875632820800776X
- Promotion of bone formation by naringin in a titanium particle‐induced diabetic murine calvarial osteolysis modelWiley: Source
- A Mediterranean Diet Enriched with Olive Oil Is Associated with Higher Serum Total Osteocalcin Levels in Elderly Men at High Cardiovascular RiskPubMed: PMC3462931
- Biochemical markers of bone resorption are present in human milk: implications for maternal and neonatal bone metabolismPubmed:25109232
- An NMR Metabolomic Study on the Effect of Alendronate in Ovariectomized MicePubmed:25184758
- Strontium Ranelate Reduces the Fracture Incidence in a Growing Mouse Model of Osteogenesis ImperfectaPubMed: 26679066
- Comparative effects of brown and golden flaxseeds on body composition, inflammation and bone remodelling biomarkers in perimenopausal overweight womenS1756464617301561
- Impact of a chronic smoking habit on the osteo-immunoinflammatory mediators in the peri-implant fluid of clinically healthy dental implants.pubmed:27328151
- Impact of a triclosan‐containing toothpaste during the progression of experimental peri‐implant mucositis: Clinical parameters and local pattern of osteo …Pubmed:29520826
- Triclosan‐containing fluoride toothpaste on clinical parameters and osteo‐inflammatory mediators when applied in a stent during experimental peri‐implant mucositis …Pubmed: 30659666
- AAV-anti-miR-214 prevents collapse of the femoral head in osteonecrosis by regulating osteoblast and osteoclast activitiesPubmed: 31739209
- Material-Dependent Formation and Degradation of Bone Matrix—Comparison of Two CryogelsPubmed: 32517006
- Comparable Effects of Strontium Ranelate and Alendronate Treatment on Fracture Reduction in a Mouse Model of Osteogenesis Imperfecta33506016
- Effects of icariin on the fracture healing in young and old rats and its mechanism34511043
- Gujiansan Ameliorates Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head by Regulating Autophagy via the HIF-1α/BNIP3 Pathway34512780