ELISA Kit DIY Materials for Procollagen II C-Terminal Propeptide (PIICP) 
P2CP; C-Propeptide Of Type II Procollagen; Procollagen II Carboxy Terminal Propeptide
- UOM
- FOB US$ 837.00 US$ 1,395.00 US$ 2,511.00 US$ 4,883.00 US$ 8,370.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.KSA964Mu11
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsMain materials for "Do It (ELISA Kit) Yourself".
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryInfection immunityBone metabolismRheumatology
- Reagent Contents Capture Antibody, Biotin-labeled Competitor, Standard, Streptavidin-HRP, TMB Substrate, 96-well Plate
- Detectable SampleSerum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids.
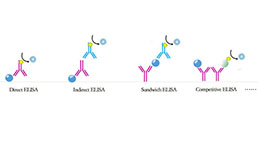
- Applicable PrincipleCompetitive Inhibition ELISA for Antigen Detection
- Detectable Range3.70-300ng/mL
- Applicable Sensitivity1.49ng/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The Abs in the kit have high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Procollagen II C-Terminal Propeptide (PIICP). No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Procollagen II C-Terminal Propeptide (PIICP) and analogues was observed.
Usage
1. Coat the plates with 100μL per well of working solution of Capture Antibody.incubate overnight at 4°C or incubate at 37°C for 2 hours.
2. Aspirate and wash 1 time.
3. Block the plates with 200 μL per well of working solution of Blocking Buffer. Incubate at 37°C for 1.5 hours.
4. Aspirate and wash 1 time. The plates are now ready for sample detection, the protocol is the same as regular ELISA.
Storage
Antibodies, Standard and Streptavidin-HRP should be stored at -20°C. TMB should be stored at 4°C. 96-well Plate could be stored at room temperature. The contents are valid for twelve months. They are stable for one month after opening when stored at 4°C.
Support pack
Giveaways
Increment services
Citations
- Evaluation of the effect of N-acetyl-glucosamine administration on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in healthy individuals without symptoms of arthritis: A …10.3892
- Evaluation of the effect of administering N-acetyl-glucosamine-containing green tea supplement on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in healthy individuals without symptoms of arthritis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study309
- Effect of N-acetylglucosamine administration on cartilage metabolism and safety in healthy subjects without symptoms of arthritis: A case reportpubmed:28413518
- Evaluation of the effect of salmon nasal proteoglycan on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in individuals with knee joint discomfort: A randomized double‑blind placebo‑controlled clinical studyetm:14
- Evaluation of the efficacy of Ajuga decumbens extract supplement in individuals with knee discomfort associated with physical activity: A randomized, double‑blind, placebo‑controlled study10.3892/etm.2017.5064
- Evaluation of the chondroprotective action of N‑acetylglucosamine in a rat experimental osteoarthritis pubmed:28912864
- Evaluation of the effect of N-acetyl-glucosamine administration on biomarkers for cartilage metabolism in healthy individuals: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical studyview/366
- No effects of hyperosmolar culture medium on tissue regeneration by human degenerated nucleus pulposus cells despite upregulation extracellular matrix genesfulltext:2018/03010
- Fibulin-3 and other cartilage metabolism biomarkers in relationship to calprotectin (MRP8/14) and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with …68362.pdf
- サケ鼻軟骨由来プロテオグリカン摂取による関節保護効果
- No Effects of Hyperosmolar Culture Medium on Tissue Regeneration by Human DegeneratedPubmed: 25856264
- Effectiveness of collagen supplementation on pain scores in healthy individuals with self-reported knee pain; A randomized controlled trialPubmed: 31990581
- Bone Morphogenetic Proteins for Nucleus Pulposus RegenerationPubmed: 32295299
- Concerted Actions by PIICP, CTXII, and TNF-¦Á in Patients with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis33924892