VOL78-Vitamin D3 and carbamazepine protect against Clostridioides difficile infection in mice by restoring macrophage lysosome acidification

On 6 January 2022, William Ka Kei Wu, Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, and his team published a paper tittled “Vitamin D3 and carbamazepine protect against Clostridioides difficile infection in mice by restoring macrophage lysosome acidification” in Autophagy, which showed that Vitamin D3 and carbamazepine protect against Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) by restoring melanocyte inducing transcription factor (MITF) expression and lysosomal function in mice.

The kits [ELISA Kit for Interleukin 8 (IL8), SEA080Hu; ELISA Kit for Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2), SEB603Hu/SEB603Mu] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.



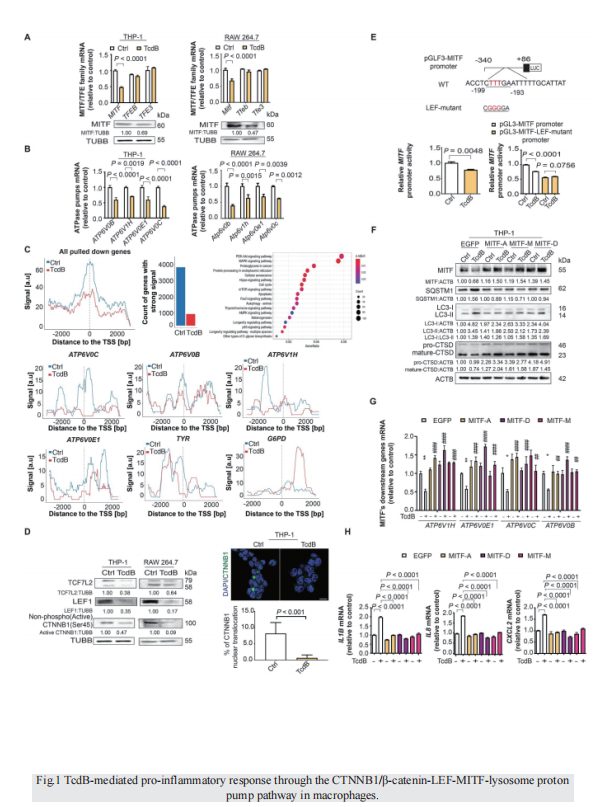
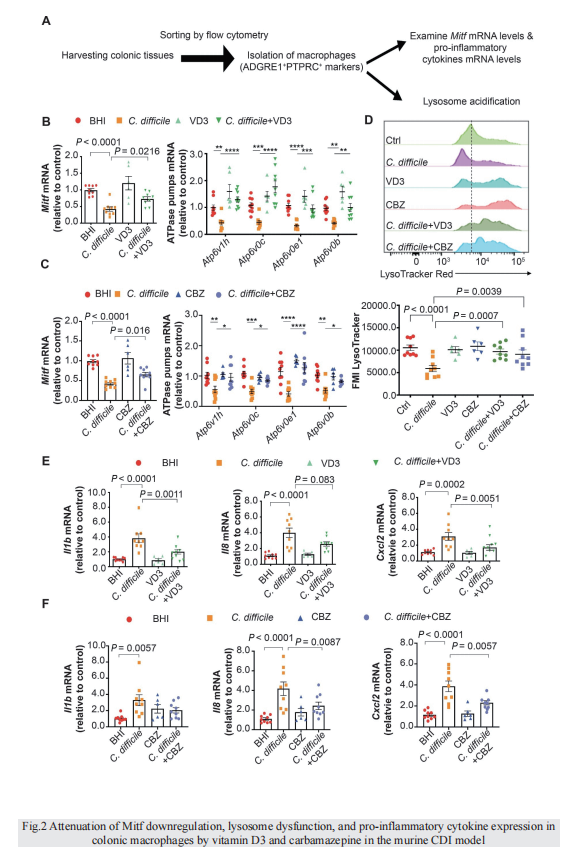
Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is a common cause of nosocomial diarrhea. TcdB is a major C. difficile exotoxin that activates macrophages to promote inflammation and epithelial damage. Lysosome impairment is a known trigger for inflammation. Herein, we hypothesize that TcdB could impair macrophage lysosomal function to mediate inflammation during CDI. Effects of TcdB on lysosomal function and the downstream pro-inflammatory SQSTM1/p62-NFKB (nuclear factor kappa B) signaling were assessed in cultured macrophages and in a murine CDI model. Protective effects of two lysosome activators (i.e., vitamin D3 and carbamazepine) were assessed. Results showed that TcdB inhibited CTNNB1/β-catenin activity to downregulate MITF (melanocyte inducing transcription factor) and its direct target genes encoding components of lysosomal membrane vacuolar-type ATPase, thereby suppressing lysosome acidification in macrophages. The resulting lysosomal dysfunction then impaired autophagic flux and activated SQSTM1-NFKB signaling to drive the expression of IL1B/IL-1β (interleukin 1 beta), IL8 and CXCL2 (chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2). Restoring MITF function by enforced MITF expression or restoring lysosome acidification with 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 or carbamazepine suppressed pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in vitro. In mice, gavage with TcdB-hyperproducing C. difficile or injection of TcdB into ligated colon segments caused prominent MITF downregulation in macrophages. Vitamin D3 and carbamazepine lessened TcdB-induced lysosomal dysfunction, inflammation and histological damage. In conclusion, TcdB inhibits the CTNNB1-MITF axis to suppress lysosome acidification and activates the downstream SQSTM1-NFKB signaling in macrophages during CDI. Vitamin D3 and carbamazepine protect against CDI by restoring MITF expression and lysosomal function in mice.