Monoclonal Antibody to E-selectin 
CD62E; CD62-E; E-Selectin; ELAM; ELAM1; ESEL; SEL-E; E-LAM; E-LAM1; E-SEL; LECAM2; Endothelial Leukocyte Adhesion Molecule 1; CD62 Antigen-Like Family Member E
Overview
Properties
- Product No.MAA029Hu22
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsWB; IHC; ICC; IP.
If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies.
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategorySignal transductionCD & Adhesion moleculeTumor immunityInfection immunity
- SourceMonoclonal antibody preparation, Host Mouse
- Ig Isotype IgG, Clone Number n/a
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelNone
- Immunogen n/a
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.02% NaN3, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid, Concentration 1mg/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The antibody is a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against E-selectin. It has been selected for its ability to recognize E-selectin in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
Usage
Western blotting: 0.2-2µg/mL;1:500-5000
Immunohistochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:50-200
Immunocytochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:50-200
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Storage
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Antibody Labeling Customized Service
Antibody Labeling Customized Service
-
 Protein A/G Purification Column
Protein A/G Purification Column
-
 Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
-
 Positive Control for Antibody
Positive Control for Antibody
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
-
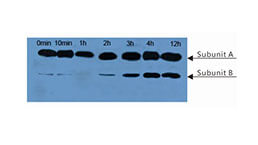 Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
-
 Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
-
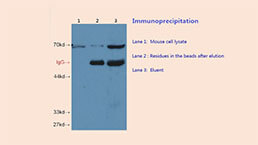 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 DAB Chromogen Kit
DAB Chromogen Kit
-
 SABC Kit
SABC Kit
-
 Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Citations
- Systemic involvement of high-mobility group box 1 protein and therapeutic effect of anti-high-mobility group box 1 protein antibody in a rat model of crush injury.PubMed: 22392147
- Endothelial gene expression and molecular changes in response to radiosurgery in in vitro and in vivo models of cerebral arteriovenous malformationsPubmed: 24199192
- Evaluation of the effects of Eserine and JWH-133 on brain dysfunction associated with experimental endotoxemiaPubMed: 25867462
- Serum lipid profile and inflammatory markers in the aorta of cholesterol-fed rats supplemented with extra virgin olive oil, sunflower oils and oil-productsPubMed: 26401576
- Adhesion molecules, chemokines and matrix metallo-proteinases response after albendazole and albendazole plus steroid therapy in swine neurocysticercosispubmed:28821422
- Evaluating Platelet Activation Related to the Degradation of Biomaterials Using Molecular MarkersPubmed: 32812629
- The role of the adipocytokines vaspin and visfatin in vascular endothelial function and insulin resistance in obese childrenPubmed: 31771561
- Association between Upper-airway Surgery and Ameliorative Risk Markers of endothelial function in obstructive Sleep ApneaPubmed: 31882827
- Hyperoside Protects Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Against Anticardiolipin Antibody-Induced Injury by Activating AutophagyPubmed: 32508661
- Effect of liraglutide on microcirculation in rat model with absolute insulin deficiency34119534
- Effect of dipeptide on intestinal peptide transporter 1 gene expression: An evaluation using primary cultured chicken intestinal epithelial cells34309968
- Construction of a rabbit model with vinorelbine administration via peripherally inserted central catheter and dynamic monitoring of changes in phlebitis and thrombosisPubmed:35126715





