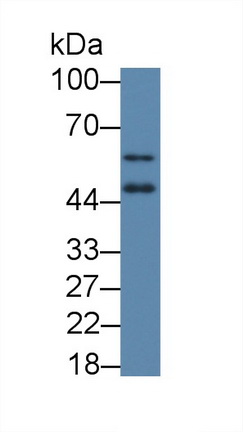
Polyclonal Antibody to Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) 
NR1I1; Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group I Member 1; Calcitriol Receptor; 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor
Overview
Properties
- Product No.PAA475Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsWB
If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies.
Research use only - DownloadInstruction Manual
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayEndocrinology
- SourcePolyclonal antibody preparation, Host Rabbit
- Ig Type IgG, Potency n/a
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelNone
- Immunogen RPA475Hu01-Recombinant Vitamin D Receptor (VDR)
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.02% NaN3, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid, Concentration 0.5mg/ml
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against VDR. It has been selected for its ability to recognize VDR in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
Usage
Western blotting: 0.01-2µg/mL;
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Storage
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Organism Species More: Mus musculus (Mouse)Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Antibody Labeling Customized Service
Antibody Labeling Customized Service
-
 Protein A/G Purification Column
Protein A/G Purification Column
-
 Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
-
 Positive Control for Antibody
Positive Control for Antibody
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
-
 Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
-
 Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 DAB Chromogen Kit
DAB Chromogen Kit
-
 SABC Kit
SABC Kit
-
 Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Citations
- The vitamin D receptor: A therapeutic target for the treatment of breast cancer?Cgi: Content
- Vitamin D receptor as a target for breast cancer therapy.pubmed:28213567
- Effect of exercise on serum vitamin D and tissue vitamin Dreceptors in experimentally induced type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.pubmed:27504197
- Vitamin D supplementation attenuates oxidative stress in paraspinal skeletal muscles in patients with low back painPubmed:29143122
- Enhanced remedial effects for vitamin D3 and calcium co-supplementation against pre-existing lead nephrotoxicity in mice: The roles of renal calcium homeostatic …Pubmed: 30553018
- Seluang Fish (Rasbora Spp.) Oil Decreases Inflammatory Cytokines Via Increasing Vitamin D Level in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Status of vitamin D and the associated host factors in pulmonary tuberculosis patients and their household contacts: a cross sectional studyPubmed: 31255688
- Association of Fok1 VDR polymorphism with Vitamin D and its associated molecules in pulmonary tuberculosis patients and their household contactsPubmed: 31649297
- Vitamin D Status in Dupuytren's Disease: Association with Clinical Status and Vitamin D Receptor Expression
- Betok Fish (Anabas testudineus) Oil Decreases Inflammatory Cytokine through Increasing Vitamin D Level in Rats-induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Positive Correlation between Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and C-Reactive Protein in Vitamin D Deficient Preterm Infants with Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Identification of SNP of VDR and VDBP gene and its Dysregulated pathway through VDR-VDBP interaction network analysis in Vitamin D deficient Infertile …