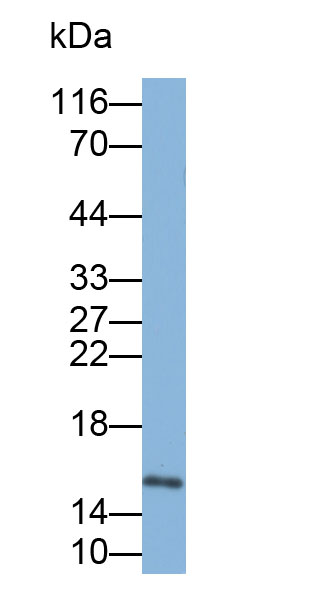
Biotin-Linked Polyclonal Antibody to Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 (FABP4) 
A-FABP; AFABP; AP2; Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4, Adipocyte; Adipocyte Protein 2; Adipocyte-type fatty acid-binding protein
- UOM
- FOB US$ 132.00 US$ 308.00 US$ 440.00 US$ 1,100.00 US$ 4,400.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.LAB693Po71
- Organism SpeciesSus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsWBIf the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies.
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayEndocrinologyCardiovascular biologyHepatology
- SourceAntibody labeling
- Ig Type IgG, Potency n/a
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelBiotin
- Original Antibody PAB693Po01-Polyclonal Antibody to Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 (FABP4)
- Buffer Formulation0.01M PBS, pH7.4, containing 0.05% Proclin-300, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid, Concentration 500µg/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against FABP4. It has been selected for its ability to recognize FABP4 in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
Usage
Western blotting: 0.01-2µg/mL;
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Storage
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Protein A/G Purification Column
Protein A/G Purification Column
-
 Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
-
 Positive Control for Antibody
Positive Control for Antibody
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
-
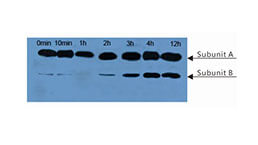 Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
-
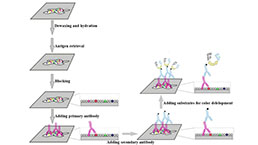 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
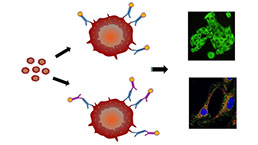 Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
-
 Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
-
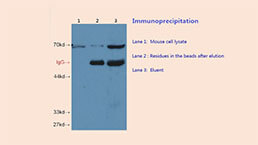 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 DAB Chromogen Kit
DAB Chromogen Kit
-
 SABC Kit
SABC Kit
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Citations
- Enhanced A-FABP expression in visceral fat: potential contributor to the progression of NASHPubMed: 23091808
- Siesta is associated with reduced systolic blood pressure level and decreased prevalence of hypertension in older adultsPubMed: 26134622
- Overexpression of the A-FABP gene facilitates intermuscular fat deposition in transgenic micePubMed: 25867423
- Cranberries (Oxycoccus quadripetalus) inhibit lipid metabolism and modulate leptin and adiponectin secretion in 3T3-L1 adipocytesPubMed: 25952883
- Increased expression of fatty acid binding protein 4 in preeclamptic Placenta and its relevance to preeclampsiaPubmed:26992681
- Valproate acid (VPA)-induced dysmetabolic function in clinical and animal studies.pubmed:28161274
- Changes of Plasma FABP4, CRP, Leptin, and Chemerin Levels in relation to Different Dietary Patterns and Duodenal-Jejunal Omega Switch Surgery in Sprague …Pubmed:29849871
- Lack of pronounced changes in the expression of fatty acid handling proteins in adipose tissue and plasma of morbidly obese humansPubmed:29335416
- 25-HC promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through up-regulation of TLR4 dependent FABP4Pubmed: 31720079
- Water Specific MRI T1 Mapping for Evaluating Liver Inflammation Activity Grades in Rats With Methionine‐Choline‐Deficient Diet‐Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver …Pubmed:35212074
- The Effect of Mineralocorticoid Receptor 3 Antagonists on Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fatty Acid Transport Profile in Patients with Heart FailurePubmed:35455943
- FABP4 secreted by M1-polarized macrophages promotes synovitis and angiogenesis to exacerbate rheumatoid arthritisPubmed:35729106