FITC-Linked Polyclonal Antibody to Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1) 
SEPP; SeP; SEP-P1; SELP
- UOM
- FOB US$ 139.00 US$ 325.00 US$ 464.00 US$ 1,160.00 US$ 4,640.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.LAB809Hu81
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsWB; IHC; ICC; IF.If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies.
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryMetabolic pathwayInfection immunity
- SourceAntibody labeling
- Ig Type IgG, Potency n/a
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelFITC
- Original Antibody n/a
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.02% NaN3, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid, Concentration 500µg/mL
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Specifity
The antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against SEPP1. It has been selected for its ability to recognize SEPP1 in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
Usage
Western blotting: 0.2-2µg/mL;1:250-2500
Immunohistochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:25-100
Immunocytochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;1:25-100
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Storage
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Stability
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Protein A/G Purification Column
Protein A/G Purification Column
-
 Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
-
 Positive Control for Antibody
Positive Control for Antibody
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
-
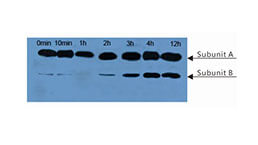 Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
-
 Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
-
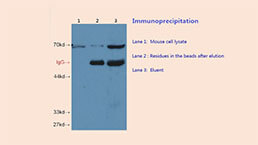 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 DAB Chromogen Kit
DAB Chromogen Kit
-
 SABC Kit
SABC Kit
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Citations
- Serum Selenoprotein P Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes: Implications for Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and AtherosclerosisPubMed: 21677040
- Increased Selenoprotein P Levels in Subjects with Visceral Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver DiseasePubMed: 23439771
- Trace elements, heavy metals and vitamins in Egyptian school children with iron deficiency anemiaMetapress:Source
- Selenium and its relationship with selenoprotein P and glutathione peroxidase in children and adolescents with Hashimoto's thyroiditis and hypothyroidismPubMed: 26854239
- Selenoprotein P is elevated in individuals with obesity, but is not independently associated withinsulin resistance.pubmed:27524654
- Acute Overfeeding Does Not Alter Liver or Adipose Tissue-Derived Cytokines in HealthyHumans.pubmed:27832637
- DNA damage and oxidative stress response to selenium yeast in the non-smoking individuals: ashort-term supplementation trial with respect to GPX1 and SEPP1 polymorphism.pubmed:26658762
- Evaluation of the Relationship Between Insulin Resistance and Selenoprotein P in Patients with Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDOI: 10.14744/scie.2017.87597
- Serum selenium and selenoprotein-P levels in autoimmune thyroid dieases patients in a select center a transversal studyDOI: 10.1590/2359-3997000000309
- Selenium, selenoproteins and selenometabolites in mothers and babies at the time of birthpubmed:28534447
- Biomarkers of selenium status and antioxidant effect in workers occupationally exposed to mercuryPubmed:29895371
- Comparison of Human Selenoprotein P Determinants in Serum between Our Original Methods and Commercially Available KitsPubmed:29709922
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the first trimester and subsequent development of gestational diabetes mellitusPubmed: 30470912
- Selenium Levels in Community Dwellers with Type 2 Diabetes MellitusPubmed: 30725267
- Can hepatokines be regarded as novel non-invasive serum biomarkers of intrahepatic lipid content in obese children?Pubmed: 30921653
- Acute swimming exercise, but not exposure to moderate hypoxic conditions reduces circulating selenoprotein P levels in short-term, high-fat diet-fed ratsPubmed: 31236416
- Selenium and selenoprotein P in nonalcoholic fatty liver diseasePubmed: 31493247
- Soil Selenium Concentration and Residents Daily Dietary Intake in a Selenosis Area: A Preliminary Study in Yutangba Village, Enshi City, ChinaPubmed: 32909074
- Higher Serum Selenoprotein P Level as a Novel Inductor of Metabolic Complications in PsoriasisPubmed: 32605214
- Circulating hepassocin level in patients with stable angina is associated with fatty liver and renal function
- Selenium–GPX4 axis protects follicular helper T cells from ferroptosis34413521
- Selenoprotein P-1 (SEPP1) as An Early Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Cardiopulmonary Bypass





