Mouse Model for Cerebral Hemorrhage (CH) 
Hemorrhage, Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- UOM
- FOB US$ 200.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.DSI836Mu01
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsDisease Model
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryCerebral and nervous systems
- Prototype SpeciesHuman
- Sourceinduced by Collagenase
- Model Animal StrainsC57BL/6 Mice(SPF), healthy, male, age: 6~8 weeks, body weight:22g~25g.
- Modeling Grouping1.Randomly divided into six group: Control group, Model group, Positive drug group and Tested drug group.
- Modeling Period1w
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Modeling Method
The mice were anesthetized by intrabitoneal injection. 1uL of 0.1mg/mL type IV collagenase solution was injected through brain stereolocalization (the former fontanel site was at zero, 2.2mm to the left, 1.0mm forward, and 2.7mm into the needle). After the injection, the needle was kept in situ for 10 minutes to prevent collagenase reflux, and then the needle was slowly withdrawn.The body temperature of mice was maintained at 37℃ during the whole experiment.
ICH model and SHAM group were prepared, except for no collagenase injection, other operations were the same.(Note that collagenase should be placed on an ice pack to keep the temperature low)
Model evaluation
Neurological function detection and assessment:
The 5-point system of Longa and Bederson was used to score the animals 24h after waking up from anesthesia. The higher the score, the more serious behavior disorder of the animals.
0 points: no symptoms of nerve damage
1 point: Can't fully extend the opposite forepaw
2 points: Turn to the opposite side
3 points: Tip to the opposite side
4 points: inability to walk spontaneously, loss of consciousness
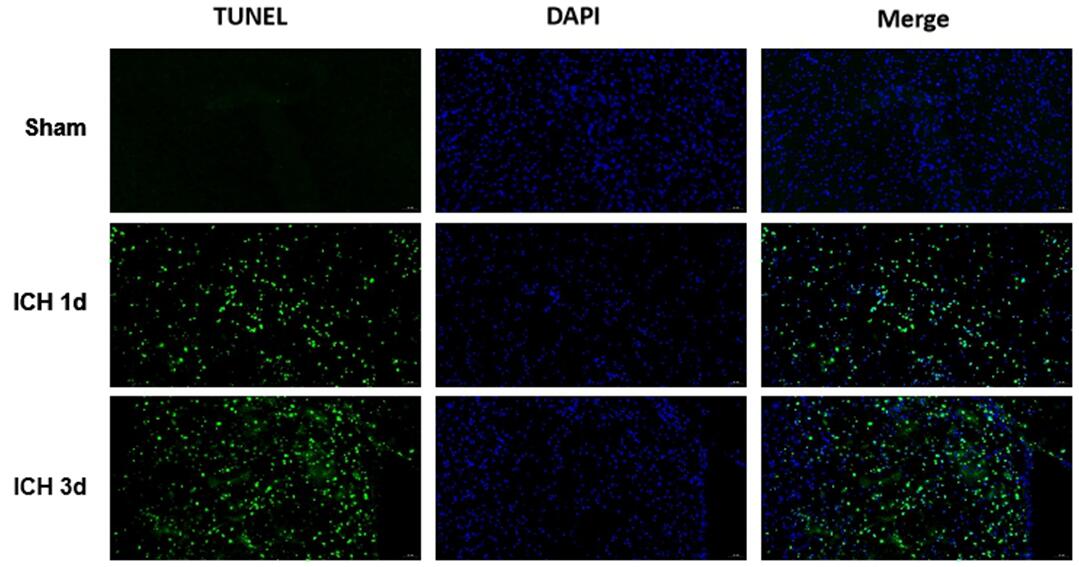
Pathological results
HE staining: the tissue morphology of the bleeding site was detected.
Prussian blue staining: determine bleeding in the molding area;
The expression of NeuN (neuron marker), GFAP (astrocyte marker) and Iba1 (microglia marker) in brain tissues were detected by immunohistofluorescence staining.
Apoptosis detection: Tunel fluorescence staining was used to detect the apoptosis of brain tissue.
Cytokines level
Statistical analysis
SPSS software is used for statistical analysis, measurement data to mean ± standard deviation (x ±s), using t test and single factor analysis of variance for group comparison , P<0.05 indicates there was a significant difference, P<0.01 indicates there are very significant differences.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
-
 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
-
 Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
-
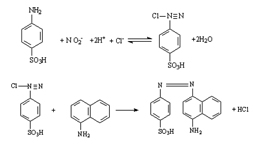 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
-
 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
-
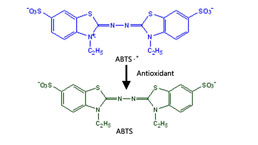 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
-
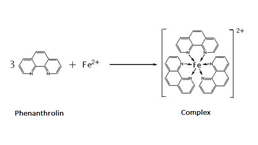 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
-
 Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
-
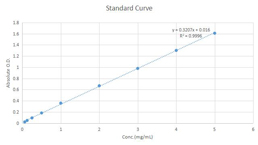 Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
-
 Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
-
 Catalase Assay Kit
Catalase Assay Kit
-
 Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
-
 Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
-
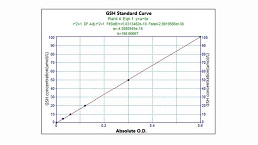 Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
-
 Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
-
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
-
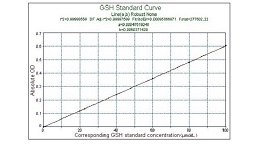 Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
-
 Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits