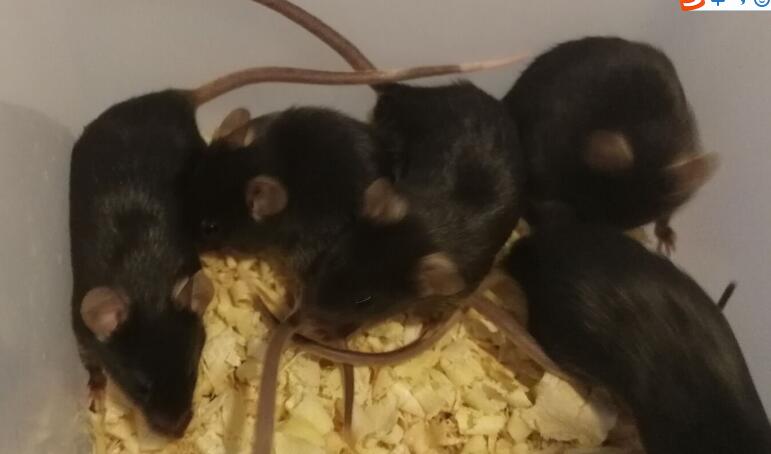
Mouse Model for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) 
- UOM
- FOB US$ 140.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.DSI626Mu01
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsDisease Model
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- CategoryRespiratory system
- Prototype SpeciesHuman
- SourceInduced by LPS
- Model Animal StrainsC57bl/6 Mice (SPF), healthy, male, age: 8~10weeks, body weight:30g~35g.
- Modeling GroupingRandomly divided into six group: Control group, Model group, Positive drug group and Test drug group.
- Modeling Period1 week
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Modeling Method
Mouse were anesthetized via enterocoelia and injected LPS (6mg/kg) into lung using the method of exposure tracheotomy dripping. Then revolve mouse vertically to diffuse LPS at lung evenly. Building the mouse model for endotoxic acute lung injury. Perhaps LPS given to mouse via caudal vein or enterocoelia, building the mouse ARDS model induced by systemic inflammatory response.
6 hours, 12 hours, 24 hours and 48 hours after LPS dripping, take 3 mouse respectively. Collect bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissue.
Sample collection:
BALF: After blood collection, open its chest, separate mediastina, inject 3ml saline from trachea to the lung. Every time lavage thrice, collect the douche. Centrifuged it at 4℃, 3000r/min for 15 min, take the supernatant.
Lung tissue: Mouse were anesthetized via enterocoelia, the anticoagulant treatment were carried out with 1ml heparinized saline through the right ventricular cavity, and different lung tissues were taken from the chest immediately.
Model evaluation
Diff-Quik staining and cell count:
Obtained BALF for Diff-Quik staining, observation and count of neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes.
Wet/dry weight ratio of lung:
Wet/dry weight ratio of lung directly reflect pneumonedema, and also reflect severity of lung injury. Kill mouse, cut their weasand, take complete lung and weigh wet. Then dry the lung in a 65 ℃ incubator, 24h later weigh weigh dry and count wet/dry weight ratio of lung.
Determination of lung permeability by Evans blue:
30min before the end of the experiment, intravenous injection of Evans blue (EBD, 30mg/kg), After the experiment, open chest and cut right chamber, wash lesser circulation, take double lung completely, cut off the trachea, clean and dry lung tissue. Homogenate after weighing, soaking lung tissue homogenate with 1ml formamide per 100mg lung tissue, incubated at 37℃ for 24h, centrifuge at 5000r/min, take supernatant to measure EBD concentration.
Pathological results
Histopathology observation of lung injury (HE staining)
Take the right lung, 4% poly formaldehyde solution fixed, embedded to make the paraffin section (5μm), HE staining.
Scoring methods: Bleeding and edema scores were obtained from 6 fields.
Cytokines level
Detect the concentration of TNF-a, IL-6 and IL-1β in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) by ELISA.
Statistical analysis
SPSS software is used for statistical analysis, measurement data to mean ± standard deviation (x ±s), using t test and single factor analysis of variance for group comparison , P<0.05 indicates there was a significant difference, P<0.01 indicates there are very significant differences.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
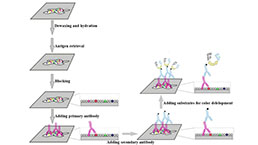 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
-
 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
-
 Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
-
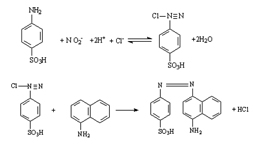 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
-
 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
-
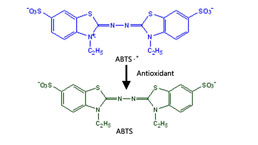 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
-
 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
-
 Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
-
 Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
-
 Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
-
 Catalase Assay Kit
Catalase Assay Kit
-
 Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
-
 Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
-
 Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
-
 Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
-
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
-
 Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
-
 Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits







