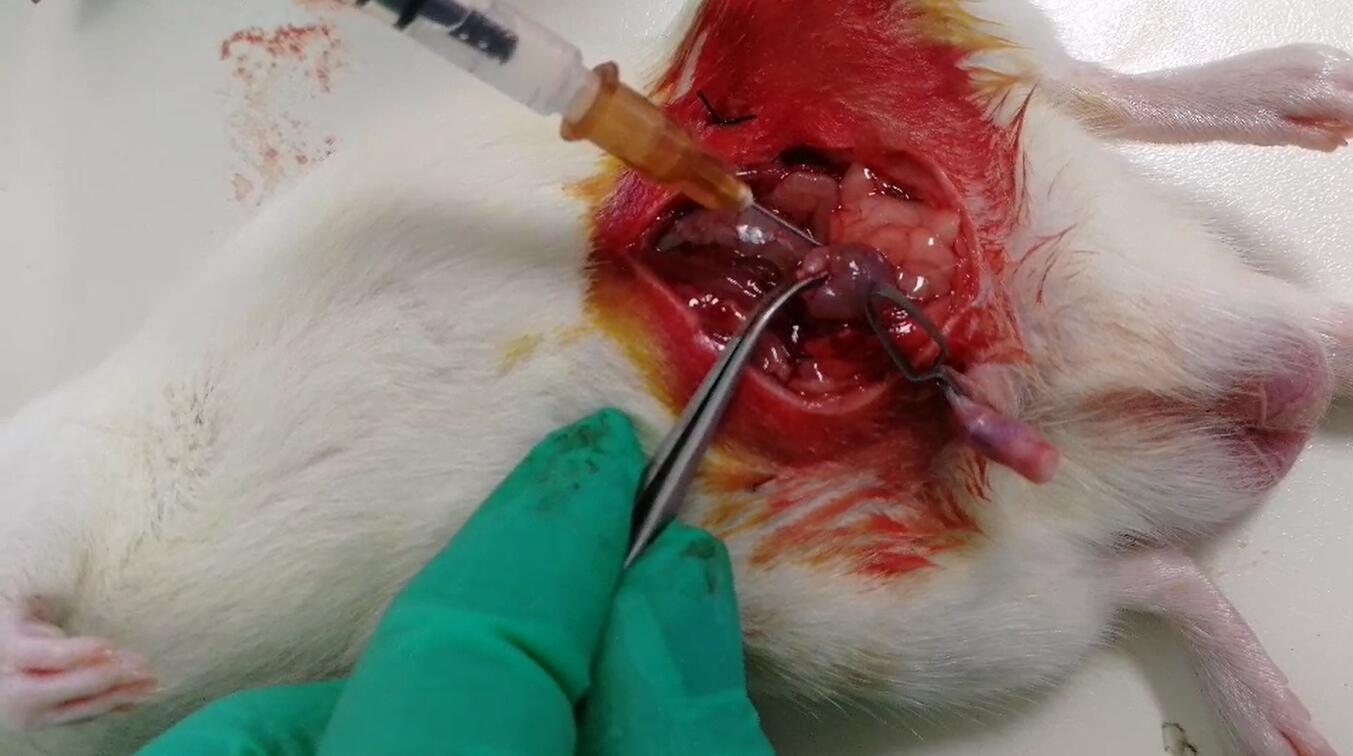
Rat Model for Acute Pyelonephritis (AP) 
Pyelitis; Nephritis
- UOM
- FOB US$ 260.00
- Quantity
Overview
Properties
- Product No.DSI559Ra01
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- ApplicationsDisease Model
Research use only - Downloadn/a
- Category
- Prototype SpeciesHuman
- Sourceinduced by bacterial infections
- Model Animal StrainsSD Rats(SPF), healthy, male and female, body weight 180g~200g.
- Modeling GroupingRandomly divided into six group: Control group, Model group, Positive drug group and Test drug group.
- Modeling Period4-6 weeks
Sign into your account
Share a new citation as an author
Upload your experimental result
Review

Contact us
Please fill in the blank.
Modeling Method
Rats weight is 200 g, prohibit drinking water after 24 h. After anesthesia, the animal was supine and fixed on the operating table, abdominal skin was disinfected, sterile surgical towels were spread, and a 2cm incision was made in the middle of the lower abdomen. The abdominal wall was cut layer by layer into the abdominal cavity, and the right ureter was identified on the right posterior abdominal wall.4 suture silk thread was used to thread the needle from both sides of the right middle ureter to the lateral side of the posterior abdominal wall and lead the suture line. The penis was clipped with an artery clamp, and 0.5mL EScherichia coli(Escherichia coli,ATCC 25922) liquid of 600 nm = 0.35 ~ 0.40 was slowly injected into the bladder with TB needle.Then, the ends of the suture line outside the abdominal wall were tightened to make the ureter shrink to 1/3, and the suture line was pulled to the back of the rat to tie the knot. The incision in the abdominal wall was sutured layer by layer to restore drinking water and food supply. 24h after the operation, the ligature line outside the abdominal wall was removed and the ureter was reopened.
The animals were killed at a predetermined time, both kidneys were taken, and the renal capsule was carefully removed. Then, the kidney was cut longitudinally, half of the kidney was homogenized for bacterial culture, and the other half was fixed in fixative solution, routine tissue section, HE staining, and light microscope observation. Urine bacterial culture was performed by bladder puncture at the same time.
Model evaluation
Bacteriological examination:
Sterile urine was absorbed 20μ L and coated on a plate for culture. 24 hours later, 1/4 colony was scraped and dissolved in 25mL normal saline. Detect 600nm absorbance. Normal saline was used as blank control.
One side of the kidney tissue was cut 200mg, 10ml of sterile water homogenate was added, 100 μ L of homogenate was absorbed and placed in a petri dish. The medium was sterilized by high pressure steam at 121℃, cooled to 50-60 ℃, then poured into the petri dish and gently shaken, and cultured in a biochemical incubator at 37℃ for 24h. The results were scored by semi-quantitative method. A bacterial count > 10000 was considered positive, and a bacterial count < 500 was considered negative.
Pathological results
HE staining:
One side of kidney tissue was taken, fixed and embedded, paraffin section was performed, and HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of kidney tissue.
Cytokines level
Statistical analysis
SPSS software is used for statistical analysis, measurement data to mean ± standard deviation (x ±s), using t test and single factor analysis of variance for group comparison , P<0.05 indicates there was a significant difference, P<0.01 indicates there are very significant differences.
Giveaways
Increment services
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
-
 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
-
 Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
-
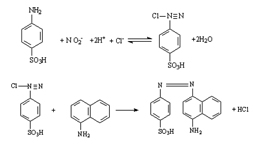 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
-
 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
-
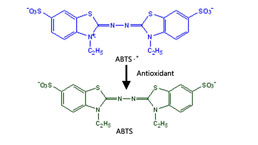 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
-
 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
-
 Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
-
 Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
-
 Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
-
 Catalase Assay Kit
Catalase Assay Kit
-
 Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
-
 Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
-
 Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
-
 Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
-
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
-
 Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
-
 Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits